UI/UX is the first place where your users are going to be exposed to your product, which means that if you do not have the basics of UI/UX done right, you are going to have a bad first impression. This is especially important for businesses that are trying to target the millennial demographics.
Outline of the blog-
Here is an in-depth video you can check out on UI/UX Basics

The product development process involves a series of steps to take a product from an idea to a commercialized product in the market, where product managers, designers, stakeholders, developers all work together on the product. This process is often initiated by the conception of the need for a new product or service that could be beneficial for customers.
The major responsibility of the designer must be to create the best version of a requested product, with the time and resources they have at hand. It is the fact that, if you are going to create a product and introduce it to a market where there is competition, you must create a better product and not just a simple MVP. The MVP (Minimum Viable Product) is dead, long life to MAP (Minimum Awesome Product).
The best way to see this approach is with an example:-
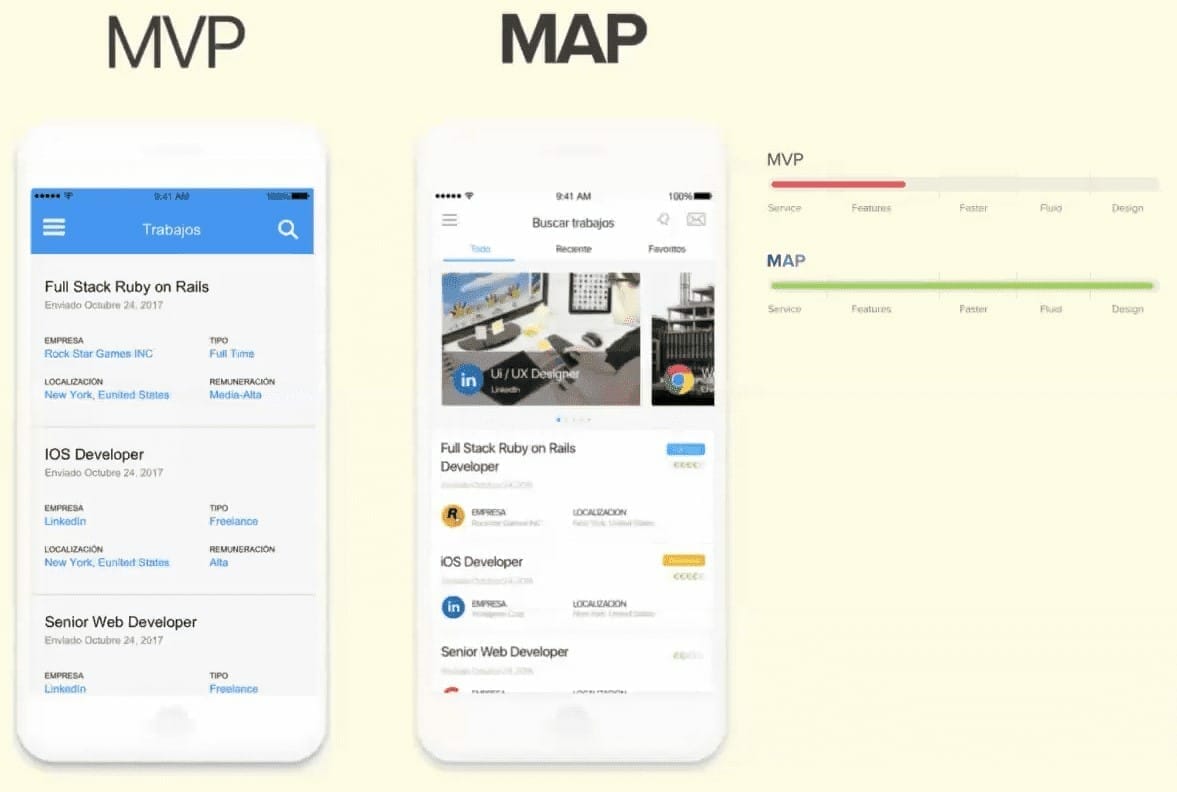
What are the differences between the two products?
They are really showing the same content, but both have:- Header and Item of employment (which includes: name, date, company, type and remuneration).
But it seems more reliable and attractive in MAP to the user/end customer.
“The true competition is to offer a better experience on our product.”
And a better experience includes everything: features, speed, fluidity and design. This is essential to compete for head to head with other apps.
UX is a conceptual design discipline, which means apart from being aesthetically pleasing it also has certain responsibilities towards its users. UX delivers a lot more than fulfilling the primordial duties of the product.
User Experience Design (UX) is the process of enhancing user satisfaction during the interaction between the user and the product, which makes it a highly important supporting discipline of the process of product development.
UX design is not only about how a platform looks and feels, but also how it works. It includes elements that are seen or touched, such as the layout of a website or the design of an app’s buttons, features, and icons as well as elements that are not visual, such as the logic behind the interface, the placement of buttons etc. UX designers are responsible for determining what features are most important to users, how they should work in relation to each other, and which ones are the most important to emphasize.
Design is everywhere and that’s why you can take inspiration from everything in your surroundings. Photographs of nature. It’s a well-known fact that nature is the best inspiration. So you can take your favorite shot and get a color scheme out of it.
“Most people make the mistake of thinking design is what it looks like,” the designers are handed this box and told, ‘Make it look good!’ That’s not what we think design is. It’s not just what it looks like and feels like. Design is how it works.”
User experience focuses on the experience that users have while using products like websites, apps, and physical objects. designers make those everyday interactions more useful, usable, and accessible to users.
The value of UX design is immense; not only for the end-user but also for the business or brand behind the user experience.
From a user perspective, good UX design ultimately enables us to go about our daily lives as effortlessly as possible. From setting an alarm to chatting with friends online, listening to music or using a calendar app, the ease with which we complete these actions is the result of good design.
When designing these experiences, designers must consider how they can bring value to all kinds of users.
The next big fact of UX is that it’s everywhere
Design is not limited to the digital world, but instead everything we use in our daily life.
OVAN will you still love it just because it looks good? No. If it is not easy to use, then its appearance means nothing to you.
Understanding how to make an oven easy and safe to use when users are cooking the food is also the designer’s responsibility.
To give users what they need is the first goal of user experience design. Before using a product, people are mostly concerned about “whether it is useful?” “Will this product solve my problems?” So a product should meet the functional demands of users first.
For example, Facebook at the beginning didn’t take “making friends with strangers (say, a friend’s friend)” seriously as they believed that people only have curiosity about their surroundings. However the data show that most users like to expand their circles by adding strangers as their friends, and now they have added that feature.
“Will I get what I want in the most simple, direct and quick way?” It would be better if you “Don’t make me think”.
40% of shoppers surveyed think their shopping experience would be better if retailers offered a wishlist where they can save items they’re interested in.
User Experience design is a process that focuses on enhancing customer experience by improving usability, accessibility, and pleasure provided in the interaction between the customer and the product. The key responsibilities of a User Experience designer are to focus on customer goals and business goals.
User Interface Design refers to the visual elements of a digital product. It focuses on anticipating what users might need to do and ensuring that the interface has elements that are easy to access, understand and use to facilitate those actions.
| UX | UI |
| Competitor analysis | Understanding of UX design process and research |
| Customer analysis and user research | Customer analysis |
| Product structure, information architecture | Design Research |
| Sketching, low-Fidelity Wireframes | Branding and graphic development |
| High-Fidelity wireframing and design | |
| Adaption to all device screen sizes | |
| Coordination and implementation with developers |
A Design Sprint is a proven, scientific process of collaborative brainstorming which helps in assessing which features to build first and which ones to eliminate. It helps in saving development time and money by solidifying concepts and building the groundwork for wireframing and designing.
Here are the steps of a typical Design Sprint. To shorten the time and dependency on resources we focus on the most critical DEFINE-DIVERGE-DECIDE steps during a typical sprint.
Competitive analysis is a critical part of the research process, whether it is of any domain understanding the landscape of solution is crucial to the foundation of solutions you are designing.
The competitive analysis provides a strategic insight into the features, functions, flow, and emotions aroused by your competitors’ design solutions. By understanding these components of competitor products, you can design your solution with the goal of creating a quality product and/or knowledge.
Competitive analysis is a way of assessing the strengths and weaknesses of a product compared to other competitors. It involves looking around competing products to compare between to determine what is effective when compared with the set of predefined conditions.
In the first step of our design sprint process, we take inputs from our clients and get to know more about their competitors. Learn about the process they follow and try to find gaps and opportunities so that we can capitalize on those points.
You can create a shortlist of main comparison criteria before you start. You can always add more criteria if it makes sense. This will keep your research guided. Basically, you have to enlist all the features of your product, find similar products or products with similar features and then find out what new features others have and what new features we have and how well they are implemented. Remember to add the product you’re designing to the analysis to see how your product compares to the competition. Start with 3-5 main competitors. Identify any UX issues with a competitor’s product and create a comprehensive list. This list will help you learn from other people’s mistakes.
Persona is a method of modeling, summarizing and communicating research by people who have been observed or researched in some way. It is a customer-type representation. People answer the question, “Who are we designing?” and they help to align strategies with goals in certain user groups.
At Mindbowser, we take initiative to understand more about the users of the app, what is their motive behind using the app and what are their goals. Based on the inputs and our desk research, we create user personas for the project.
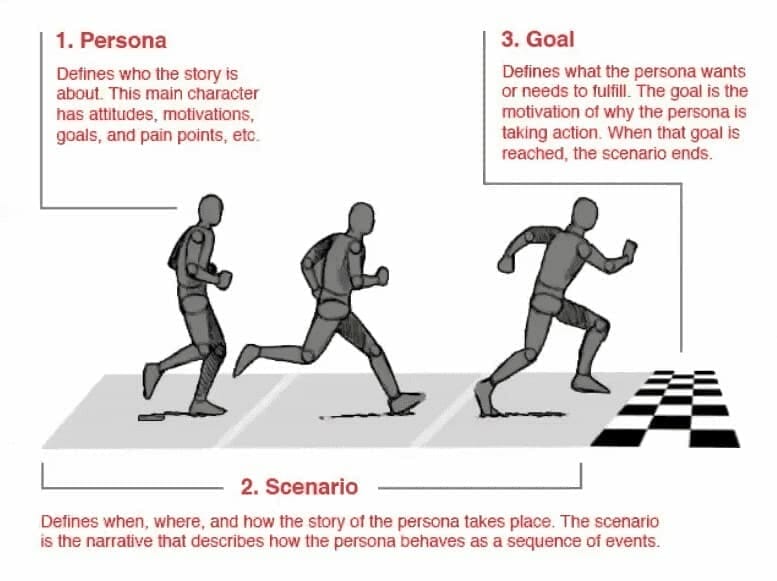
A Persona is the representation of our ideal user, whenever we face a roadblock we can go back to these personas who act like our ideal user and from there we can analyze the main pain points of our users, what exactly is stopping them from using our product or what expectations they have from the platform that we are going to build.

The art and science of editing and labeling websites, intranets, online communities and software to support usability and accessibility.
The IA is:
Information architecture (IA) is the structural design of shared information environments. A well-structured information environment is usable, findable, and useful. Thus, it requires an architect who can establish the most appropriate organization of information for its intended users and purposes.
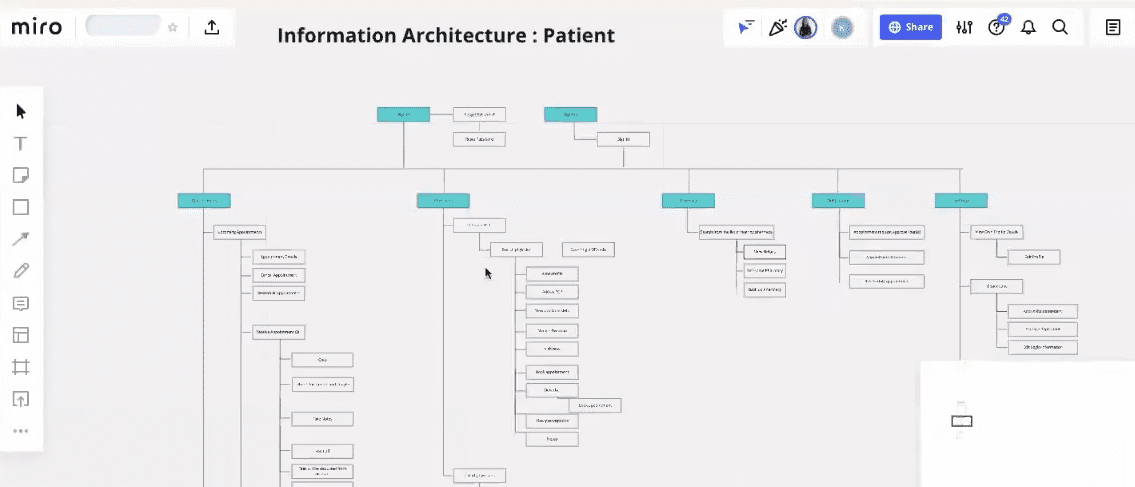
In this figure you can see that it’s an IA for an application where Notifications and settings are 2 categories shown under which different content is structured under settings section there uses a view’s own profile and dependent section whereas in the notification section there is Reminder, reschedule Appointment request.
Wireframing is an essential tool we use in our project scope definition and app development process. It allows us to clearly map out where the most important elements in the application should be and simplifies communication between the design team, product owner and the development team. It helps designers spot potential issues in the structure or flow of your application.
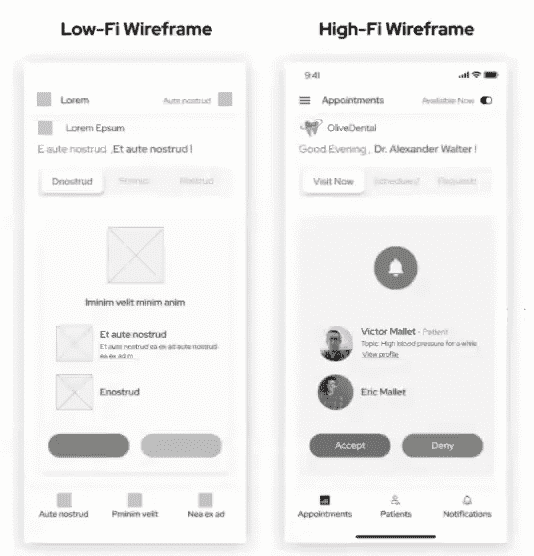
When you create a clickable prototype of the complete platform called ‘wireframes’. Wireframes are black and white blueprints of the application. They are like your real app but with no code. Through wireframes, you finalize your app, and each screen and activity associated comes to life.
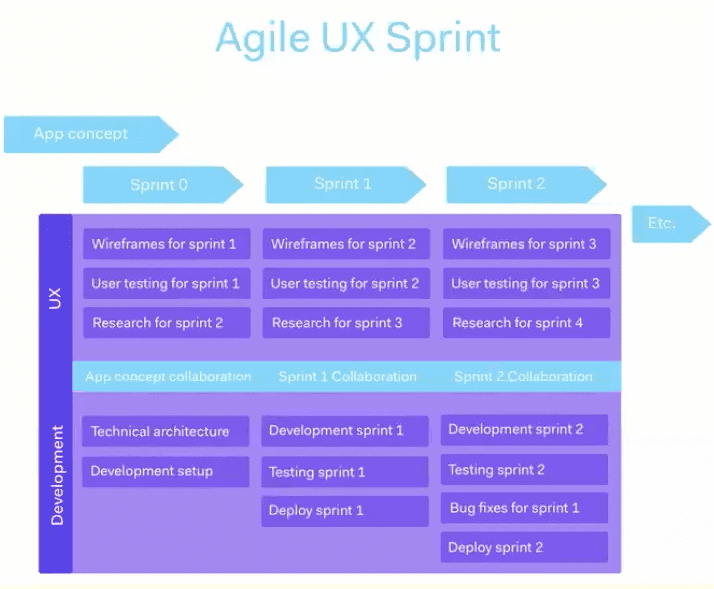
Agile UX is a collaborative process that optimizes digital products by delivering value early and often. It’s a way to design, develop, and deliver digital solutions that customers love while getting valuable feedback along the way.
Agile UX builds upon the concepts of Agile development by adding elements from User Experience design into the process. Agile UX focuses on bringing design into the Agile process. This means the design is actually carried out using sprints, scrums and retrospectives – the same framework a development team will be using. Agile UX is iterative, so can prevent big upfront designs from being handed over to development teams. Therefore, designers are less likely to go off on their own, and design in isolation to feedback from the rest of the team. An example of an Agile UX alongside development may look like this:
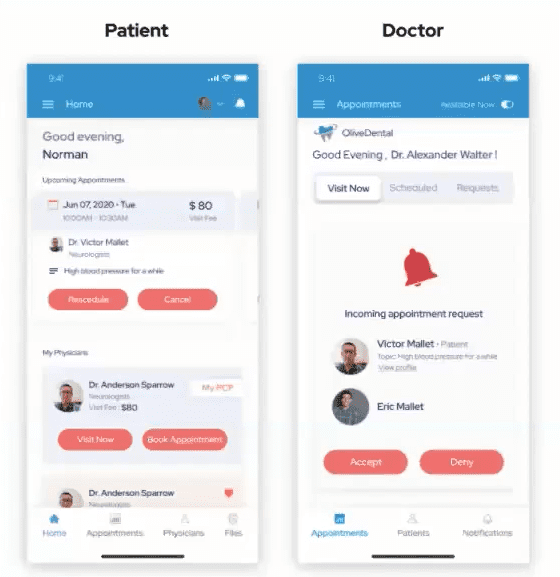
UX design is the practice of enhancing user satisfaction by improving the usability, accessibility, and pleasure provided in the interaction between the user and the product. UI design is the art of creating sites, applications, and digital products that are both functional and visually appealing. They essentially go hand in hand.
User Experience Design is a business function. It comes into play once the business decides to employ user experience design into its product. The foundation of a successful user experience design is a clearly articulated strategy, which stems from clearly defined business goals.
Every business has certain goals in mind. This set of goals that the organization aims to achieve are Business Goals. Only when you understand the business goals of your project, will you be able to design the right product or service for your users and organization.
Read Related: 19 Healthcare UI/UX Design Practices to Keep in Mind for Telehealth Apps

Hope you like our in-depth article on the basics of UI/UX for the product development implementation process. Also, you can contact the Mindbowser team for UI/UX design services and to understand the process of the Design Sprint methodology.
This Blog was written by Vaishnavi Yannawar & Vishvajit Sande of the Mindbowser UI/UX team and modified by the Mindbowser Content team for publication purposes.

We worked with Mindbowser on a design sprint, and their team did an awesome job. They really helped us shape the look and feel of our web app and gave us a clean, thoughtful design that our build team could...


The team at Mindbowser was highly professional, patient, and collaborative throughout our engagement. They struck the right balance between offering guidance and taking direction, which made the development process smooth. Although our project wasn’t related to healthcare, we clearly benefited...

Founder, Texas Ranch Security

Mindbowser played a crucial role in helping us bring everything together into a unified, cohesive product. Their commitment to industry-standard coding practices made an enormous difference, allowing developers to seamlessly transition in and out of the project without any confusion....

CEO, MarketsAI

I'm thrilled to be partnering with Mindbowser on our journey with TravelRite. The collaboration has been exceptional, and I’m truly grateful for the dedication and expertise the team has brought to the development process. Their commitment to our mission is...

Founder & CEO, TravelRite

The Mindbowser team's professionalism consistently impressed me. Their commitment to quality shone through in every aspect of the project. They truly went the extra mile, ensuring they understood our needs perfectly and were always willing to invest the time to...

CTO, New Day Therapeutics

I collaborated with Mindbowser for several years on a complex SaaS platform project. They took over a partially completed project and successfully transformed it into a fully functional and robust platform. Throughout the entire process, the quality of their work...

President, E.B. Carlson

Mindbowser and team are professional, talented and very responsive. They got us through a challenging situation with our IOT product successfully. They will be our go to dev team going forward.

Founder, Cascada

Amazing team to work with. Very responsive and very skilled in both front and backend engineering. Looking forward to our next project together.

Co-Founder, Emerge

The team is great to work with. Very professional, on task, and efficient.

Founder, PeriopMD

I can not express enough how pleased we are with the whole team. From the first call and meeting, they took our vision and ran with it. Communication was easy and everyone was flexible to our schedule. I’m excited to...

Founder, Seeke

We had very close go live timeline and Mindbowser team got us live a month before.

CEO, BuyNow WorldWide

If you want a team of great developers, I recommend them for the next project.

Founder, Teach Reach

Mindbowser built both iOS and Android apps for Mindworks, that have stood the test of time. 5 years later they still function quite beautifully. Their team always met their objectives and I'm very happy with the end result. Thank you!

Founder, Mindworks

Mindbowser has delivered a much better quality product than our previous tech vendors. Our product is stable and passed Well Architected Framework Review from AWS.

CEO, PurpleAnt

I am happy to share that we got USD 10k in cloud credits courtesy of our friends at Mindbowser. Thank you Pravin and Ayush, this means a lot to us.

CTO, Shortlist

Mindbowser is one of the reasons that our app is successful. These guys have been a great team.

Founder & CEO, MangoMirror

Kudos for all your hard work and diligence on the Telehealth platform project. You made it possible.

CEO, ThriveHealth

Mindbowser helped us build an awesome iOS app to bring balance to people’s lives.

CEO, SMILINGMIND

They were a very responsive team! Extremely easy to communicate and work with!

Founder & CEO, TotTech

We’ve had very little-to-no hiccups at all—it’s been a really pleasurable experience.

Co-Founder, TEAM8s

Mindbowser was very helpful with explaining the development process and started quickly on the project.

Executive Director of Product Development, Innovation Lab

The greatest benefit we got from Mindbowser is the expertise. Their team has developed apps in all different industries with all types of social proofs.

Co-Founder, Vesica

Mindbowser is professional, efficient and thorough.

Consultant, XPRIZE

Very committed, they create beautiful apps and are very benevolent. They have brilliant Ideas.

Founder, S.T.A.R.S of Wellness

Mindbowser was great; they listened to us a lot and helped us hone in on the actual idea of the app. They had put together fantastic wireframes for us.

Co-Founder, Flat Earth

Ayush was responsive and paired me with the best team member possible, to complete my complex vision and project. Could not be happier.

Founder, Child Life On Call

The team from Mindbowser stayed on task, asked the right questions, and completed the required tasks in a timely fashion! Strong work team!

CEO, SDOH2Health LLC

Mindbowser was easy to work with and hit the ground running, immediately feeling like part of our team.

CEO, Stealth Startup

Mindbowser was an excellent partner in developing my fitness app. They were patient, attentive, & understood my business needs. The end product exceeded my expectations. Thrilled to share it globally.

Owner, Phalanx

Mindbowser's expertise in tech, process & mobile development made them our choice for our app. The team was dedicated to the process & delivered high-quality features on time. They also gave valuable industry advice. Highly recommend them for app development...

Co-Founder, Fox&Fork
