Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain-based program that has smart contract functionality. Ethereum is open source and used to support the second-largest cryptocurrency in the world, also called Ether. Ethereum permits the smart contracts and applications built on its blockchain to run smoothly without fraud, downtime, control, or third-party interference.
Ethereum is a technology for building apps, holding assets, transacting and communicating without being controlled by a central authority. Ethereum has its cryptocurrency, Ether, used to pay for activities on the Ethereum network.
1. Banking For All
Ethereum provides a decentralized virtual banking system for all.
2. A More Private Internet
You do not need to provide all your personal information to use the Ethereum application . Ethereum is building an financial system based on value, not custodianship.
3. A Network Of Peers
Ethereum allows you to transfer money or make transactions directly with other people. You don’t need the middlemen.
4. Anti-Censorship
No government or industry has control over Ethereum. That sepration makes it virtually impossible for anyone to prevent you from receiving payments or using services on Ethereum.
5. Trade Assurance
Customers have a built-in, secure guarantee that funds will only change hands if you provide what is agreed upon. Likewise, developers can be confident that the rules won’t change for them.
6. All Products Can Be Combined
Since all applications are built on the same blockchain with shared global state, they can build on top of each other (like Legos). This helps to continuously create better products and experiences.
Ethereum is not controlled by any entity. Instead, they are controlled by nodes of computers. Several pieces come together to ensure that Ethereum works accordingly.
Ethereum’s main goal is to create a system where smart contracts, rather than a central authority, manage the programmes. When specific criteria are satisfied, smart contracts will automatically carry out their stated actions without the involvement of a third party. Smart contracts are related to any cryptocurrency. They are unrestricted and can be used outside of Ethereum, but they are known for their use of Ethereum.
It is the history of all executed smart contracts. Hundreds of nodes around the world store a copy of the entire blockchain. Thousands of computers process a smart contract each time it is executed to ensure that all stated rules have been met. Nodes don’t just store transaction details. The account, smart contract code, and smart contract state are also stored in one node. All nodes follow the same set of rules to verify a transaction, and they are all connected to each other.
The process of producing a block of transactions to add to the Ethereum blockchain is known as mining. The word mining originated in the similar context of gold to cryptocurrency. Gold or precious metals are very rare, as are digital tokens, and the only way to increase the total volume is through mining.
This is also relevant because in Ethereum the only method of release after launch is through mining. However, unlike these examples, mining is also a way to secure the network by creating, verifying, publishing, and propagating blocks in the blockchain.
Ether Mining = Network Security
Ethereum currently employs a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism. Mining is the bedrock of proof of work. Ethereum miners’ computers run software that uses their time and computing power to process transactions and generate blocks.
Related Read: How Blockchain Is Changing The Healthcare Industry?
Ethereum 2.0 is an better version of the existing Ethereum cryptocurrency. It is developed with the motive of improving the scalability, speed, and efficiency of Ethereum. The new version is conceive to work on raising transaction numbers and addressing bottlenecks. Serenity and Eth2 are some of the short names for Ethereum 2.0.
Ethereum used to employ the Proof-of-work (PoW) consensus technique, whereas Ethereum 2.0 is based on sharding and the Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanism. Ethereum 2.0 will be fully functional and the expected date to merge is around 15-September-2022.
Sharding: The process of dividing a blockchain into multiple blockchains is called sharding. Some blockchains in Ethereum 2.0 are commonly referred to as shards. Partitioning allows the entire network to act as a single validator to handle the entire workload as a single entity or process.
There are different validators and each validator must maintain its shard to keep track of the information. Unlike blockchain blocks, validators are scrambled to prevent data tampering or manipulation. To make the different segments coordinate and communicate, a chain is used, known as the Beacon Chain.
Proof of Stake: Previously, the proof-of-work consensus method was used in Ethereum, but Ethereum 2.0 introduced us to the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism. In proof-of-work, some miners mine bitcoins, while there are validators and not miners in Proof-of-stake. The validator generates new blocks with enough storage space, bandwidth, and computing power to verify and validate transactions.
Like miners, validators also receive payment for their effort and hard work in creating blocks. Validators must sign an agreement or complete a contract where validators must deposit 32 ETH, which will be locked. This is a type of bond deposited by validators that will be canceled according to the protocol in the event of fraud or negligence. This is a big improvement in Ethereum 2.0 as it will prevent bad behavior.
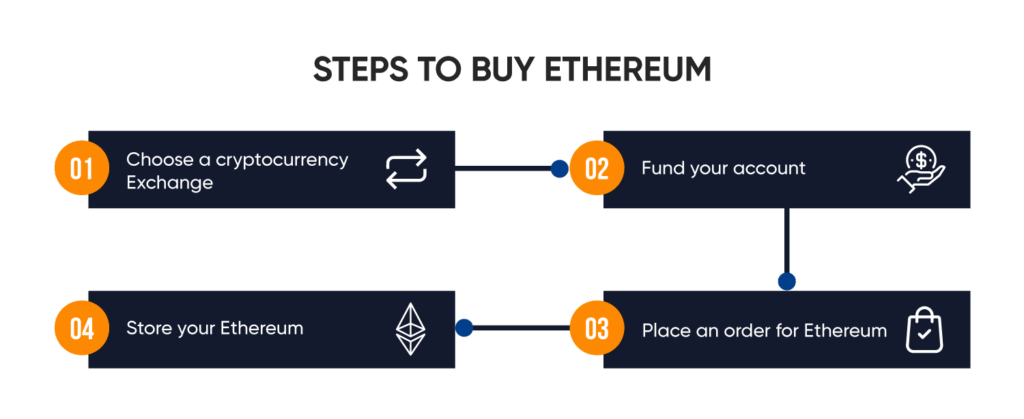
You won’t be able to buy crypto from a bank or online broker like Vanguard or Fidelity. rather, you will need a cryptocurrency trading platform. There are many cryptocurrency exchanges available, from simple dashboards to complex dashboards for advanced traders. Different platforms have different prices, security measures, and other features, so you should do your research before signing up.

In this article we learn all the basics of Ethereum blockchain, the future and use cases of Ethereum. We also learn to buy and store ether. Mining and learning about eth2.0 etc.

We worked with Mindbowser on a design sprint, and their team did an awesome job. They really helped us shape the look and feel of our web app and gave us a clean, thoughtful design that our build team could...


The team at Mindbowser was highly professional, patient, and collaborative throughout our engagement. They struck the right balance between offering guidance and taking direction, which made the development process smooth. Although our project wasn’t related to healthcare, we clearly benefited...

Founder, Texas Ranch Security

Mindbowser played a crucial role in helping us bring everything together into a unified, cohesive product. Their commitment to industry-standard coding practices made an enormous difference, allowing developers to seamlessly transition in and out of the project without any confusion....

CEO, MarketsAI

I'm thrilled to be partnering with Mindbowser on our journey with TravelRite. The collaboration has been exceptional, and I’m truly grateful for the dedication and expertise the team has brought to the development process. Their commitment to our mission is...

Founder & CEO, TravelRite

The Mindbowser team's professionalism consistently impressed me. Their commitment to quality shone through in every aspect of the project. They truly went the extra mile, ensuring they understood our needs perfectly and were always willing to invest the time to...

CTO, New Day Therapeutics

I collaborated with Mindbowser for several years on a complex SaaS platform project. They took over a partially completed project and successfully transformed it into a fully functional and robust platform. Throughout the entire process, the quality of their work...

President, E.B. Carlson

Mindbowser and team are professional, talented and very responsive. They got us through a challenging situation with our IOT product successfully. They will be our go to dev team going forward.

Founder, Cascada

Amazing team to work with. Very responsive and very skilled in both front and backend engineering. Looking forward to our next project together.

Co-Founder, Emerge

The team is great to work with. Very professional, on task, and efficient.

Founder, PeriopMD

I can not express enough how pleased we are with the whole team. From the first call and meeting, they took our vision and ran with it. Communication was easy and everyone was flexible to our schedule. I’m excited to...

Founder, Seeke

We had very close go live timeline and Mindbowser team got us live a month before.

CEO, BuyNow WorldWide

If you want a team of great developers, I recommend them for the next project.

Founder, Teach Reach

Mindbowser built both iOS and Android apps for Mindworks, that have stood the test of time. 5 years later they still function quite beautifully. Their team always met their objectives and I'm very happy with the end result. Thank you!

Founder, Mindworks

Mindbowser has delivered a much better quality product than our previous tech vendors. Our product is stable and passed Well Architected Framework Review from AWS.

CEO, PurpleAnt

I am happy to share that we got USD 10k in cloud credits courtesy of our friends at Mindbowser. Thank you Pravin and Ayush, this means a lot to us.

CTO, Shortlist

Mindbowser is one of the reasons that our app is successful. These guys have been a great team.

Founder & CEO, MangoMirror

Kudos for all your hard work and diligence on the Telehealth platform project. You made it possible.

CEO, ThriveHealth

Mindbowser helped us build an awesome iOS app to bring balance to people’s lives.

CEO, SMILINGMIND

They were a very responsive team! Extremely easy to communicate and work with!

Founder & CEO, TotTech

We’ve had very little-to-no hiccups at all—it’s been a really pleasurable experience.

Co-Founder, TEAM8s

Mindbowser was very helpful with explaining the development process and started quickly on the project.

Executive Director of Product Development, Innovation Lab

The greatest benefit we got from Mindbowser is the expertise. Their team has developed apps in all different industries with all types of social proofs.

Co-Founder, Vesica

Mindbowser is professional, efficient and thorough.

Consultant, XPRIZE

Very committed, they create beautiful apps and are very benevolent. They have brilliant Ideas.

Founder, S.T.A.R.S of Wellness

Mindbowser was great; they listened to us a lot and helped us hone in on the actual idea of the app. They had put together fantastic wireframes for us.

Co-Founder, Flat Earth

Ayush was responsive and paired me with the best team member possible, to complete my complex vision and project. Could not be happier.

Founder, Child Life On Call

The team from Mindbowser stayed on task, asked the right questions, and completed the required tasks in a timely fashion! Strong work team!

CEO, SDOH2Health LLC

Mindbowser was easy to work with and hit the ground running, immediately feeling like part of our team.

CEO, Stealth Startup

Mindbowser was an excellent partner in developing my fitness app. They were patient, attentive, & understood my business needs. The end product exceeded my expectations. Thrilled to share it globally.

Owner, Phalanx

Mindbowser's expertise in tech, process & mobile development made them our choice for our app. The team was dedicated to the process & delivered high-quality features on time. They also gave valuable industry advice. Highly recommend them for app development...

Co-Founder, Fox&Fork
